What is thalassemia?
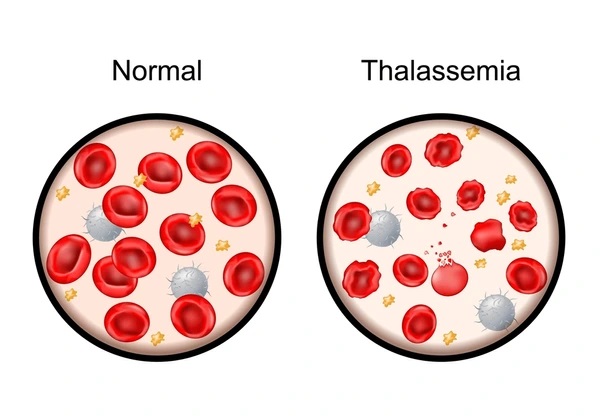
Thalassemia is an inherited blood disorder that causes the body to produce less hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that helps them carry oxygen from the lungs to all parts of the body. Hemoglobin is made up of four parts: two alpha proteins and two beta proteins. Thalassemia affects one or more of the genes that produce these proteins.
- Inherited blood disorder
- Low hemoglobin levels
- Red blood cell damage.
- Fatigue and weakness
- Frequent blood transfusions
- Iron overload complications